Introduction
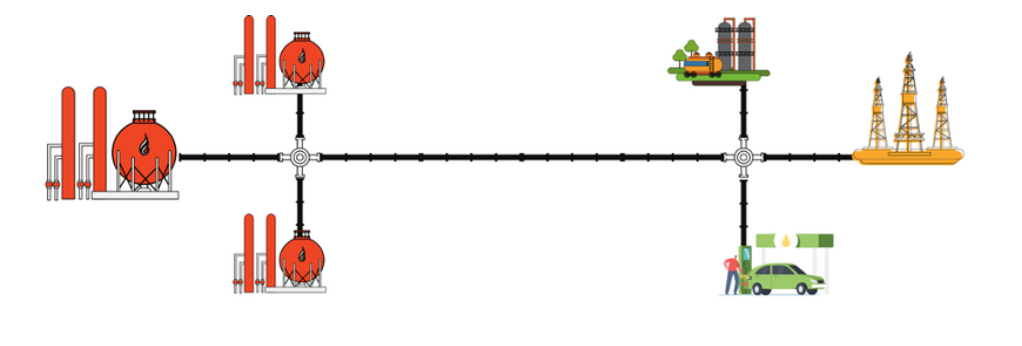
Gas Pipeline infrastructure is an economical and safe mode of transporting the natural gas by connecting gas sources to gas consuming markets. Gas pipeline grid determines the structure of the gas market and its development. Therefore, an interconnected National Gas Grid has been envisaged to ensure the adequate availability and equitable distribution of natural gas in all parts of the country. At present, there are about 17000 km long Natural Gas pipeline network which is operational in the country. In order to make available natural gas across the country, it has been envisaged to develop additional about 15,500 km pipelines to complete the National Gas Grid and same are at various stages of development. This would ensure easy availability of natural gas across all regions and also potentially help to achieve uniform economic and social progress.
PRESENT NATURAL GAS INFRASTRUCTURE IN INDIA
Common Carrier Pipelines:
These pipelines are typically built and operated by private third-party companies or government agencies, and they are open to all users for transporting natural gas. Common carrier pipelines serve as a transportation network that connects natural gas producers, suppliers, and consumers. These pipelines are designed to be accessible to multiple users, allowing them to transport natural gas from various sources to different destinations across the country. Common carrier pipelines play a crucial role in facilitating the movement of natural gas from production areas to distribution centres or end-use consumers.
The Gail India (“GAIL”) owns the largest network of common carrier natural Gas pipeline currently in the country. The company owns and operates 9,583 Km (approx.) of high-pressure natural gas pipelines with a transmission capacity of 167mmscmd. At around 5,503 Km in the length, GAIL’s Hazira-Vijaipur- Jagdishpur -GREP (Gas Rehabilitation and Expansion Project)- Dahej-Vijaipur HVJ/VDPL and Dahej-Vijaipur (DVPL)- Vijaipur-Dadri (GREP) Upgradation DVPL 2 & VDPL pipeline is the longest natural gas pipeline network in the country as of now operating at 100% capacity. Although there is no free capacity, this network has been unable to meet the increase in domestic natural gas supplies stemming from the commencement of production at the KG D6 field and the increase in India’s overall RLNG capacity. To solve this problem GAIL has done expansion and upgradation of its network. The rest of the country’s natural gas trunk pipeline infrastructure is operated by Pipeline Infrastructure Limited (PIL),Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL), Oil And Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC), Gujarat State Petronet Limited (GSPL), reliance gas pipeline limited (RGPL), Assam Gas Company Limited (AGCL) and Deepak fertilizers and petrochemicals corporation limited (DFPCL). Although the gas pipeline infrastructure has increased, it is still inadequate to fulfil the gas demand in the country.
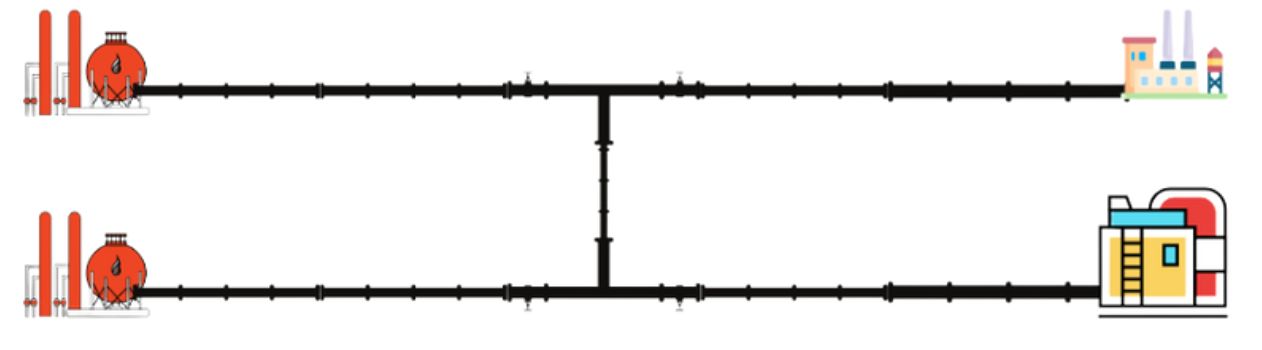
Tie-in connectivity pipelines:
Tie-in connectivity pipelines, also known as gathering pipelines, are another crucial part of the natural gas infrastructure in India. These pipelines are responsible for collecting natural gas from various wellheads or production sources and transporting it to processing plants or transmission pipelines for further distribution.
Tie-in connectivity pipelines are typically smaller in diameter compared to transmission pipelines and are used for shorter distances, usually within a particular field or production area. They are designed to connect individual gas wells or production facilities to a central gathering point or processing plant. These pipelines may also include facilities such as gas compressors, separators, and metering stations to regulate and measure the flow of natural gas.
 There are total eleven tie-in natural gas pipelines in India. This natural gas
pipeline network is operated by mainly three companies, Gas Authority Of
India, Western Concessions Private Limited and Kei RSOS Petroleum & Energy
Pvt. Ltd.. The Gas Authority of India Limited has the largest natural gas tie-in
pipeline infrastructure in the country. The company owns and operates 50 km
(approx.) of low pressure pipelines compare with common carrier natural gas
pipelines with a transmission capacity of 8.05mmscmd. At around 60km in the
length, Jaigarh – Dabhol pipeline network is the longest tie-in natural gas
pipeline operated by Western Concessions Private Limited (WCPL).
There are total eleven tie-in natural gas pipelines in India. This natural gas
pipeline network is operated by mainly three companies, Gas Authority Of
India, Western Concessions Private Limited and Kei RSOS Petroleum & Energy
Pvt. Ltd.. The Gas Authority of India Limited has the largest natural gas tie-in
pipeline infrastructure in the country. The company owns and operates 50 km
(approx.) of low pressure pipelines compare with common carrier natural gas
pipelines with a transmission capacity of 8.05mmscmd. At around 60km in the
length, Jaigarh – Dabhol pipeline network is the longest tie-in natural gas
pipeline operated by Western Concessions Private Limited (WCPL). Dedicated natural gas pipelines:
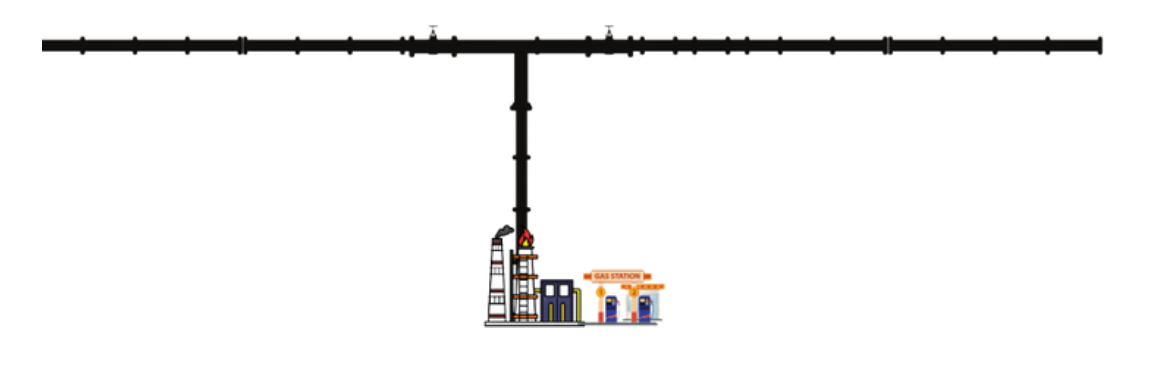
Dedicated natural gas pipelines refer to pipelines that are designed and built to transport natural gas exclusively to a specific location or plant, as opposed to pipelines that are part of a larger, interconnected network used for transporting natural gas to multiple destinations. These dedicated pipelines are typically constructed to connect natural gas production sources, such as wells or processing facilities, to a specific end-use facility, such as a power plant, industrial facility, or a specific location where the natural gas is needed.
The construction and operation of dedicated natural gas pipelines require careful planning and design to meet the specific requirements of the intended destination. This may involve considerations such as the volume of natural gas to be transported, the distance to be covered, the pressure and temperature requirements, and any specific safety or regulatory requirements at the destination facility.
Sub-transmission natural gas pipelines:
Sub-transmission natural gas pipelines are an integral part of the natural gas distribution system. These pipelines are designed to connect the main natural gas transmission lines to the city gas distribution networks, delivering natural gas from large-scale transmission lines to local distribution networks that serve homes, businesses, and other end users within a city or town.
The main purpose of sub-transmission pipelines is to transport natural gas from the transmission lines, which carry gas over long distances from gas production sources, to the city or town where it will be distributed to end consumers. These pipelines typically have smaller diameters than the main transmission lines, but larger diameters than distribution pipelines, and are often buried underground to minimize disruption to the surrounding environment.