Sloshing in Tank
Sloshing is the movement of liquid cargo inside a partially filled tank caused by the ship's motion. LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) carriers' liquid cargo is LNG, which is transported in specially designed tanks. Sloshing in LNG tanks is a significant concern in the design and operation of LNG carriers, as it can affect the stability and safety of the vessel.
Sloshing can occur in two forms: free surface and impact. Free surface sloshing occurs when the liquid inside the tank moves back and forth due to the ship's motion. Impact sloshing occurs when the liquid strikes the tank wall or structure due to abrupt changes in the ship's motion. Both types of sloshing can cause high dynamic loads and stress the tank structure, damaging the tank and the ship.
Several measures are taken to prevent the negative effects of sloshing in LNG tanks during the design and operation of LNG carriers. The tanks are designed with a sloshing mitigation system that includes baffles, surge plates, and liquid level control systems to reduce the effect of sloshing. The tanks are also filled to a certain level to minimize the free surface effect. The ship's speed and course are regulated to reduce the impact of wave motion, which can trigger sloshing. The ship's route is planned to avoid rough weather conditions, and the crew is trained to monitor and respond to any signs of sloshing.
The Problem of BOG
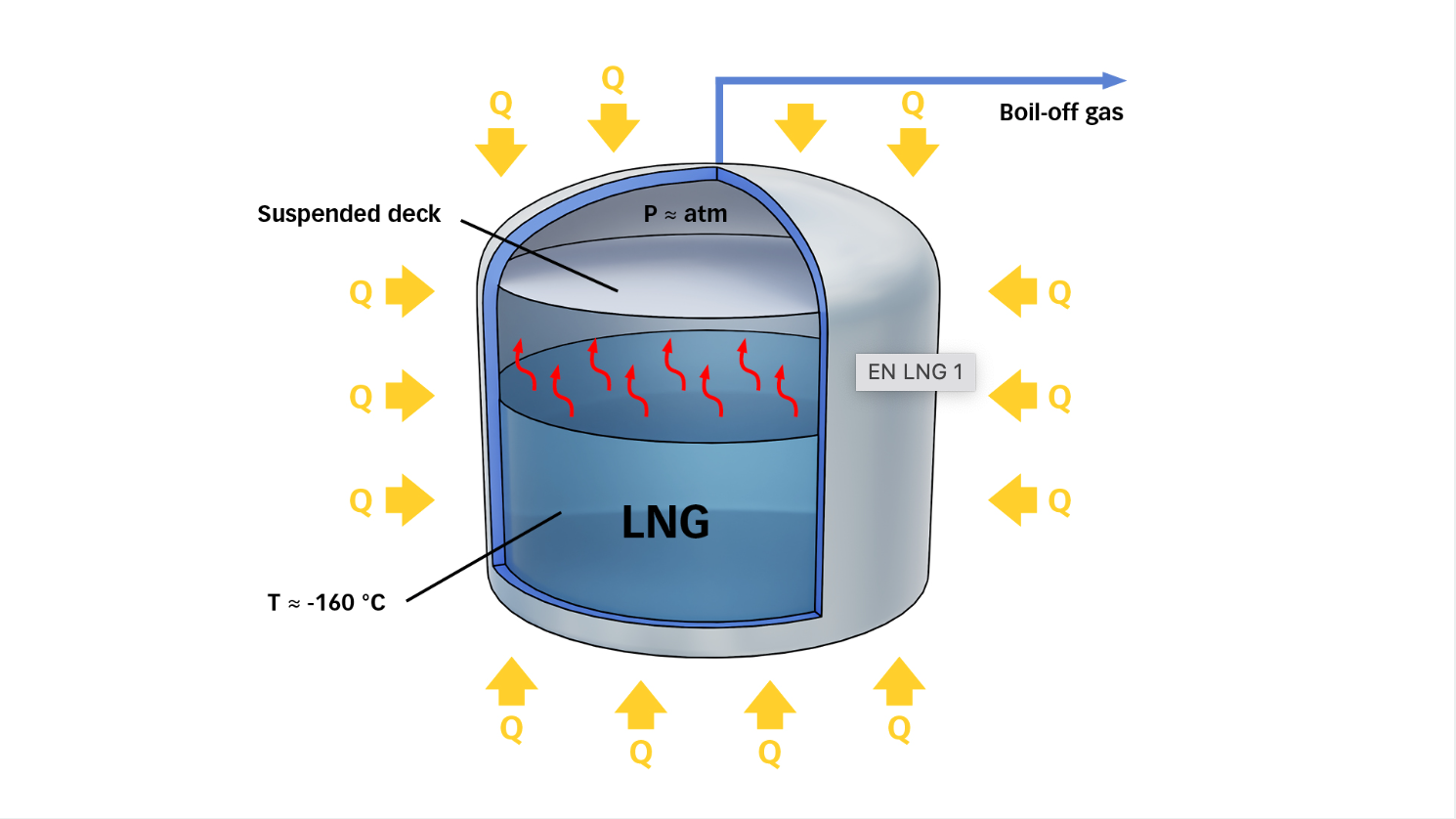
BOG stands for Boil-Off Gas, a by-product of transporting and storing Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) in insulated tanks. The BOG is generated when the LNG evaporates due to heat ingress; boil-off is a natural phenomenon that cannot be avoided entirely. The amount of BOG generated depends on several factors, such as the insulation of the tank, the temperature of the environment, the distance of the voyage, and the duration of the voyage.
BOG is a significant problem in the transportation and storage of LNG because it can cause several issues. Firstly, BOG generation can lead to a loss of LNG cargo. If the BOG is not collected and re-liquefied, it will escape into the atmosphere, wasting valuable fuel. Secondly, BOG can cause overpressure in the tank, leading to safety issues. The pressure in the tank needs to be regulated to avoid tank rupture or explosion. Thirdly, BOG can also affect the efficiency of the transportation process, as the boil-off needs to be removed or re-liquefied, which requires additional equipment and energy.
Several solutions are implemented in LNG transportation and storage. The primary solution is to collect and re-liquefy the BOG, which can be done by using a re-liquefaction plant that uses the heat of the BOG to re-cool and re- liquefy the evaporated LNG. Another solution is to use the BOG as fuel for the ship's engines, which is called Boil-Off Gas Handling System. This solution reduces the amount of BOG that needs to be collected and re-liquefied but requires additional equipment and infrastructure.
BOG Uses and Mitigation
LNG vaporization is not homogenous, and components with the lowest boiling point tend to evaporate more readily than heavier components. This phenomenon is called ageing or weathering, which changes LNG's specifications. The consequence of ageing is that the LNG composition becomes heavier, and the heating value and Wobbe Index of LNG increase over time.
BOG Uses: The BOG generated during the transportation and storage of LNG can be used in several ways. One of BOG's primary uses is fuel in the ship's dual-fuel engines. By using BOG as fuel, the amount of BOG that needs to be collected and re-liquefied can be reduced, which increases the efficiency of the transportation process. Another use of BOG is in producing steam by burning it in the boilers.
BOG Mitigation: BOG re-liquefaction is one of the primary mitigation strategies used in the LNG industry to address the issue of BOG. This process involves using a re-liquefaction plant that uses the heat of the BOG to re-cool and re-liquefy the evaporated LNG. BOG re-liquefaction can eliminate LNG shrinkage during long voyages and maintain the cargo's composition. Another mitigation strategy is to use BOG as fuel, as mentioned earlier. Additionally, the insulation of the tanks, temperature control, and route planning can also help in mitigating the BOG issue.